Principle and dosage
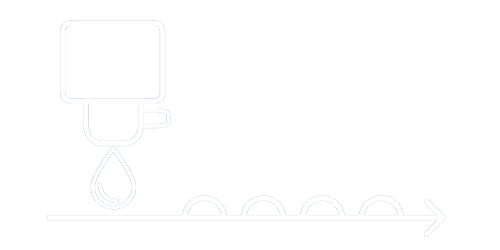
Oil quantity Q: Indicates the quantitative run of the oil dispensing through the lubricating rollers on the customer`s material
Oil quantity Qneeded: The customer`s required oil quantity Qneedes results from the amount of oil, that needs to be applied evenly over the entire spread and feed length, regardlesss of the stroke rate of the forming machine onto the material
Oil quantity Qmedium: Equal to the arithmetic mean score of the effective oil supplied
Impulse-controlled dosing
Electric oil impulse IÖ: In the conventional way of impulse-controlled dosing, the respective lubrication roller is supplied with oil by an electrically switched oil valve; the dosing unit controls the oil valve press stroke dependent.
During the activation persiod te the oil flows into the lubrication roller
Activation period te: During the activation period te the oil flows into the lubrication roller
Pause durationt tp: During the pause duration tp, the oil supply to the lubrication roller will be interrupted by closing the valve
Conclusion: Due to the pause duration tp the saturation level decreases within the lubrication roller and accordingly the oil quantity, that is released by them onto the material. Thus, the amount of oil applied by the roller does not fall below the required customer`s required oil quantity, more oil have to be supplied in the conventional impulse-controlled dosing as needed.
Dosing systems with solenoid valves - Impulse-controlled dosing: Q = f(IÖ, te, tp, n) Qmedium >> Qneeded
Integrated dosing pumps

By integrating the high precision dosing pumps, the lubrication roller are continously supplied with a constant amount of oil.
Microdosing system and precision dosing control units - dosing pump integration: Q=f(Qneeded,n) Qmedium ~Qerforderlich
 English (UK)
English (UK)  Français (France)
Français (France)  Deutsch
Deutsch  Español (España)
Español (España)  Polski (PL)
Polski (PL)  简体中文(中国)
简体中文(中国)